The electric vehicle is a reality and is currently the main global bet in the industry. With the premise of greater economy and less pollution, this vehicle has reshaped our form of mobility. Instead of fossil fuel, it uses electricity to power its engine, which is more powerful and compact, does not release exhaust gases and is practically inaudible.
Electric vehicles do not use fossil fuel for electricity, this electricity has to be sent to the vehicle in order to charge the battery and allow it to function. Car chargers and the Sunvienergy offer allow the best charging for your vehicle, with several options of power, connection, size, design and connectivity.
With Sunvienergy you will find your charger!
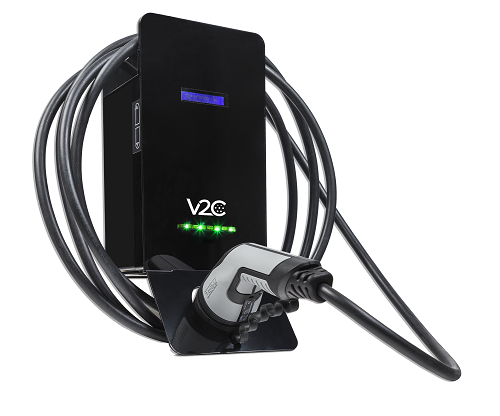

Dark is a semi-fast electric vehicle charger that can provide a power of up to 22 kW (32A three-phase). An ideal solution for charging electric vehicles in businesses, homes and also in private garages.
It allows you to control the charging speed before and during the charging process using side navigation buttons and a front screen for viewing information. In this way it is possible to modify the charging output according to the selected current.
Optionally offers the possibility of connecting with the V2C Cloud platform for online management of the charges made and also the unlocking by RFID card, in addition to other accessories and options.
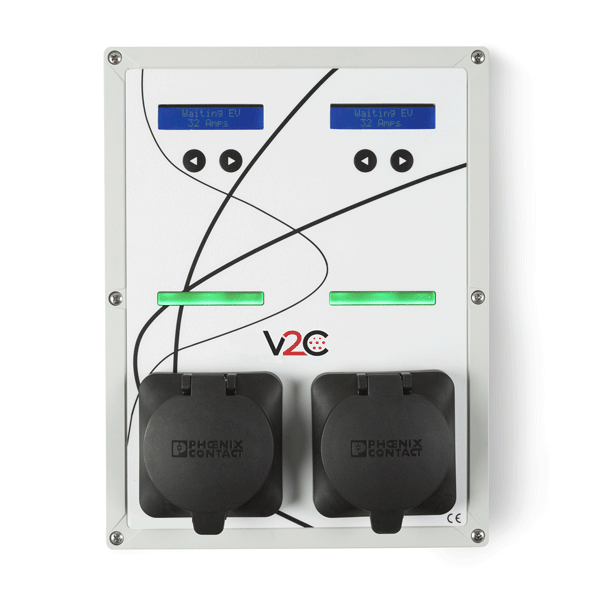
Plus is a versatile electric vehicle charger, that adapts to all your needs. It also has the possibility, depending on the model, to have one or two hoses or two connectors to charge two vehicles simultaneously in a simple solution for companies, private or community garages.
Made of highly resistant and rigid material such as ABS, acrylonitrile and butadiene styrene, Plus is the ideal solution for housing electronic components.
Like the Dark, it allows you to control the charging speed before and during the charging process, using side navigation buttons and a front screen for viewing information, making it possible to modify the charging power according to the selected current.
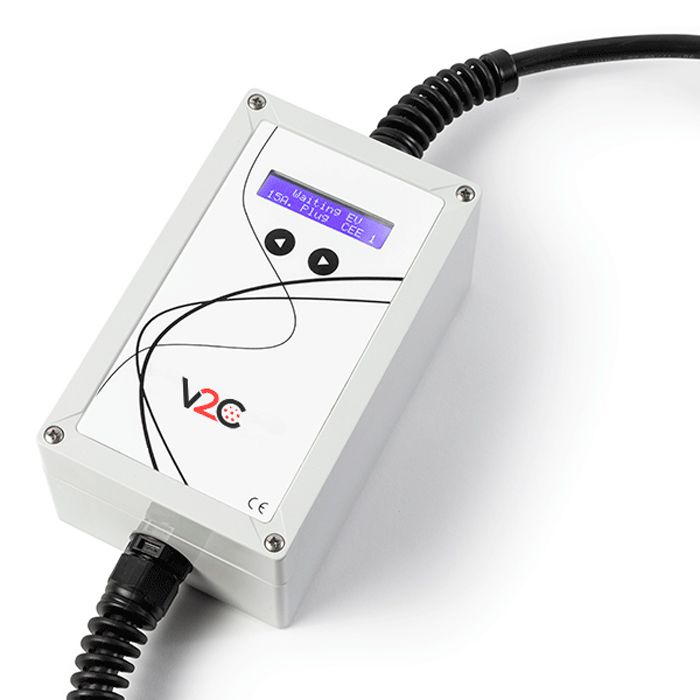

EV Portable is a portable charging device for electric vehicles. Performs a semi-fast load up to 22kW. It is the ideal solution for charging the various types of electric vehicles due to its small size and portability.
This device has an AC charger, with output connection selectable according to the car to be charged.
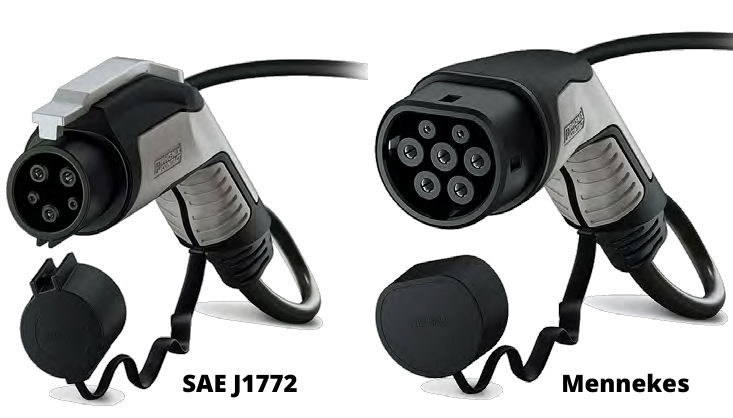
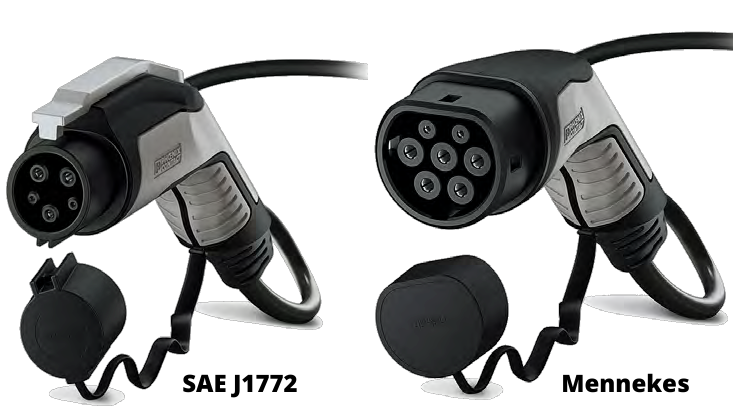
It can be traded with a Type 1 charging cable – SAE J1772 or with a Type 2 charging cable – IEC 62196 “Mennekes”.
Designed in ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), this is a material of great resistance and rigidity against impacts. It is ideal for incorporating the power electronics of the charger due to its strength and low weight.
The term Wallbox refers to the charger that supplies electricity to the vehicle connected by a cable and a connector. This device, powered by alternating current, either in single-phase or three-phase mode, brings together several components that make it a charging system for your vehicle, also called SAVE (electric vehicle power system).
The cheapest is to load vehicles in the most economical periods, that is, between 1:00 and 7:00. Anyway, the cost of charging an electric car depends fundamentally on two factors: the contracted values and the battery capacity of your electric car.
In general, each kWh has an average price that varies between € 0.15 (night) and € 0.25 (day). Therefore, to calculate how much a full battery recharge would cost, multiply the price of each kWh by the number of KWh your battery has. For example, the 2020 Renault ZOE, whose battery is 53 kWh, fully charged at night would cost approximately € 7.95, but doing so in the least economical period would cost € 13.25. In the case of ZOE, a charge allows you to cover approximately 400 km, so you would hardly spend € 3.35 / 100km.
Electric vehicles (V.E.), pure or plug-in hybrids, need an external power supply to charge the batteries. For this reason, knowing which source type to choose is important to achieve the highest efficiency of your V.E. There are currently 4 types of loading, which are explained in more detail below.
Charging Mode 1
This is a type of slow charging and is performed in a socket not specific to electric vehicles, that is, when the V.E. plugged into a domestic outlet (SCHUKO), like the one we use for other appliances.
Charging Mode 2
This type of charging uses a single-phase electrical system and is performed with a power of less than 3.7kW. The electric or hybrid vehicle is connected to the mains by means of the corresponding “charging cable”, to provide security for charging, that is, it consists of the installation of a box with a Schuko type socket, normally exclusive for charging the electric vehicle. , like our VE Portable product. This box must be connected to the protection systems suitable for the electrical network.
Charging Mode 3
Suitable for all types of electric vehicles, this charging mode requires a charging station, called WALLBOX, which has several protections for the safety of both the electrical system and the vehicle.
The electric vehicle is powered by an alternating current (AC) through a WALLBOX, being indicated for plug-in or 100% electric hybrid models. Some V.E. allow charging only in single phase, while others allow charging in both three-phase and single-phase.
For this charging mode, a specific connector is required, which will be type 1 (SAE J1772 – North American and Japanese standard) or type 2 (IEC 62196-2 – European standard), depending on the vehicle’s origin and model. Due to technological advances in terms of electricity generation and transmission, the increase in battery capacity of electric vehicles and greater safety, reliability and speed, type 3 is replacing type 2.
The choice of the ideal equipment must be made taking into account the contracted electrical power, the time available for charging the vehicle and the conditions of the installation site.
Charging Mode 4
Unlike charging types 1,2 and 3, which are carried out in alternating current (AC), charging type 4 is carried out with direct current (DC) and is normally found on highways, as it allows 80% charging of the battery. an electric vehicle in just 30 minutes, since the energy supplied to the vehicle is at least 50kW. However, although its loading speed is higher than that of the other types, type 4 is not suitable for residential use due to two main factors: (i) high equipment and installation costs, which can reach 20 thousand euros; (ii) its use should be sporadic, on a daily basis, drastically reduces the battery life of the electric vehicle.
The most common connectors are the Japanese standard CHAdeMO and the North American and European standard Combined Charging System (CCS).
The connectors used in electric vehicles depend on the vehicle, version and model. Currently, there are Type 1, Type 2 and Type 4 connectors. The Type 1 connector corresponds to the American type, also known as the SAE J1772 connector. The Type 2 connector corresponds to the European type, usually called Mennekes IEC 62196. Finally, Type 4 corresponds to the fast mode available in CHAdeMO and CCS format. In any case, the type of connector used in cars depends on the manufacturer.

In Europe, the autonomy of electric cars is governed by the WLTP (Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicle Test Procedure). This system is more demanding in the consumption register than the previous standard, which is why the indicated autonomy data is more reliable. However, despite the improvements it can be said that the real autonomy of an electric car is about 20% less than the approved one.
Each manufacturer defines the type of technology it includes in commercial vehicles and, accordingly, the electrical power absorbed during charging depends on these characteristics.
To calculate the recharge time of an electric vehicle, just know the battery capacity in kWh, the maximum absorbed power and the charger power in kW.
For example, to calculate the charging time of a Renault ZOE from 0 to 100%, with a 53kWh battery, in a three-phase AC wallbox of 22kW, just make the calculation 53/22 = 2.4 hours charging 100%. In a fast charging station (PCR) in DC, this calculation can only be done from 0 to 80%, this is because the batteries accept less power from 80%, that is, in a 50kW DC PCR the same ZOE, it takes ( 80% x 53 kWh) / 50 kW = 0.85 hours or 51 min charging 80% of the battery, for about 320km of autonomy.
The electricity needed to charge the batteries of electric vehicles can come from several sources, including zero-emission sources, such as wind, solar and water.
In this sense, we also offer photovoltaic production solutions to help you reduce your energy bill and load the vehicle and thus contribute to a better quality of the air we breathe, to reduce the emission of greenhouse gases and at the same time to reduce energy dependency.


